Which cable do I need for my electric car?
Today, more and more people are driving an electric car. It is logical, because an electric car is not only much more sustainable, but in many cases also cheaper. You no longer have to lose money for your electricity. Now it is true that you will have to charge your electric car regularly. Since not everyone is yet familiar with choosing the right cable for charging an electric car, we have listed the most important information for you in this article. By keeping this to hand, you'll find the cable you need in no time.
The different types of cables
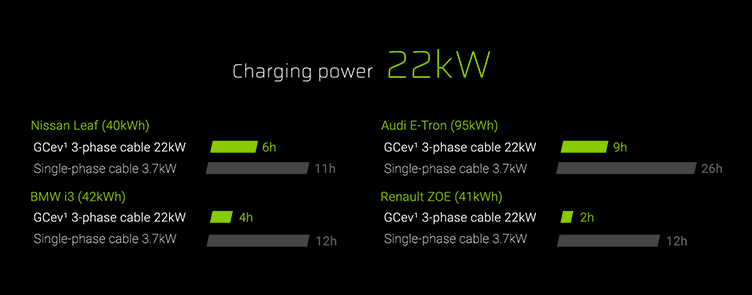
To see which types of cables are available for the electric car, it is necessary to consider the speed of the chargers. There are 3 categories of charging speeds. These are slow, fast and super fast. Slow charging can take an average of 6-12 hours at a power of about 3kW. Fast charging can take up to 4 hours to fully charge at 7kW-22kW power. The super fast can take up to an hour for a full charge at 50kW-120kW power. You can also charge alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). The cable you need depends on the type of charger being used and the vehicle's inlet port. We have listed the most important types of cables for you:
- 3 Pin connector – these cables are also known as Mode 1 or portable EV charging cables. These cables are similar to what you see with large appliances such as refrigerators and washing machines. The 3-pin plug can be plugged into a household plug while the other end is the vehicle plug. These are not used extremely often, although we see that some car manufacturers still opt for these cables.
- Type 1 – type 1 cables are the second type of cables you can find. These make it possible to charge quickly with a power of 3.7kW-7.4kW AC. The design features five different pins. This plug is usually used on car models in parts of Asia, although we sometimes see it in Europe. It can be difficult to find Type 1 chargers and charging stations in the Netherlands now that this is not the standard. This makes it a bit more difficult to drive a car with this type of charger.
- Type 2 – this is a 7 pin plug which is the standard for the European market. It offers fast charging with an output power of 3.7 kW-7 kW AC. This provides an estimated range per hour of charging of 40 kilometers. An exception to this standard are the Tesla Superchargers. They provide DC power on Type 2 terminals. The output level is 130 kW. This is a plug that is being used more and more.
- IEC 60309 – these are AC plugs commonly used with MK command sockets in Europe. The plugs are popular for high power industrial vehicle charging due to their ability to channel high voltage and current. They are also great for outdoor use as they withstand exposure to water, dirt and dust. If you have a car with this connection, it is often possible to find a charging station, which makes it possible to charge it easily.
- CCS - this is a modified and improved version of the Type 2 plug. It adds two extra power contact points that make faster charging even easier than before. These chargers allow you to choose from both AC and DC charging with an output power ranging from 50kW-350kW. The default option to choose is 50 kW.
- CHAdeMO – these cables and plugs provide fast charging with a capacity of up to 50kW DC. They are usually available at public charging stations. This type of cable is compatible with a variety of brands including Toyota, Honda, Nissan, Mazda, and Mitsubishi. Tesla Superchargers can also use this charging system, but for this you need a modified Type 2 Mennekes plug. You will of course receive this plug when you purchase your car.
Should I buy a DC or AC charging cable?
A question that many people have is whether they should have a DC cable or an AC charging cable for charging their electric car. In our country, our mains is supplied to the wall as alternating current (also known as AC). Modern electronics that we regularly use run on direct current (also known as DC). So something is needed that converts AC power from a wall outlet into DC power and converts it during charging. Direct current is also used by the batteries in an electric car. That is why a charger is integrated into the vehicle, which converts the alternating current into direct current and then into the battery pack.
For most, home charging time isn't the biggest factor, but a vehicle with a less powerful built-in charger won't charge faster through the use of smart chargers and the like. Direct DC charging is much less common, but is available at different types of charging stations. AC is converted to DC at the point of supply with power going directly to the battery. Because the on-board equipment is bypassed, loading is much faster. The downside is that this is a bit more difficult to do.

Choose the right cable for your car
We hope that the information from this article has given you a better idea when buying a good cable for your electric car. With the right cable you can be sure that you can at least charge your car in the right way. It is really important to consider the question of which cable you need. What you don't want is that you find out afterwards that you made the wrong choice. So do your research and see which cable is needed for your car.