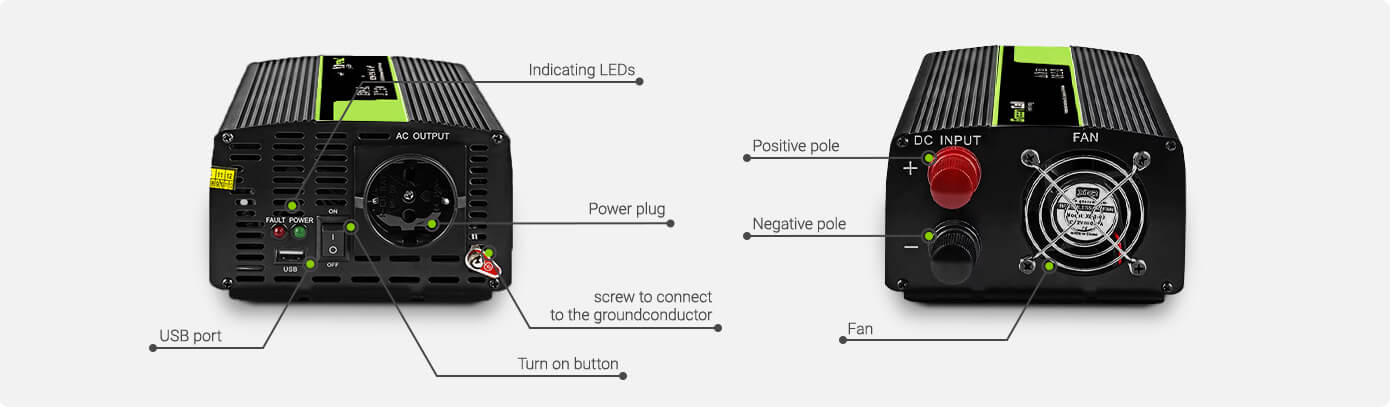
How does a voltage converter work?
Before understanding what a voltage converter is, it is important to understand the difference between AC and DC power. In simple terms, AC is what you get from the outlets in your home, and DC is what you get from batteries.
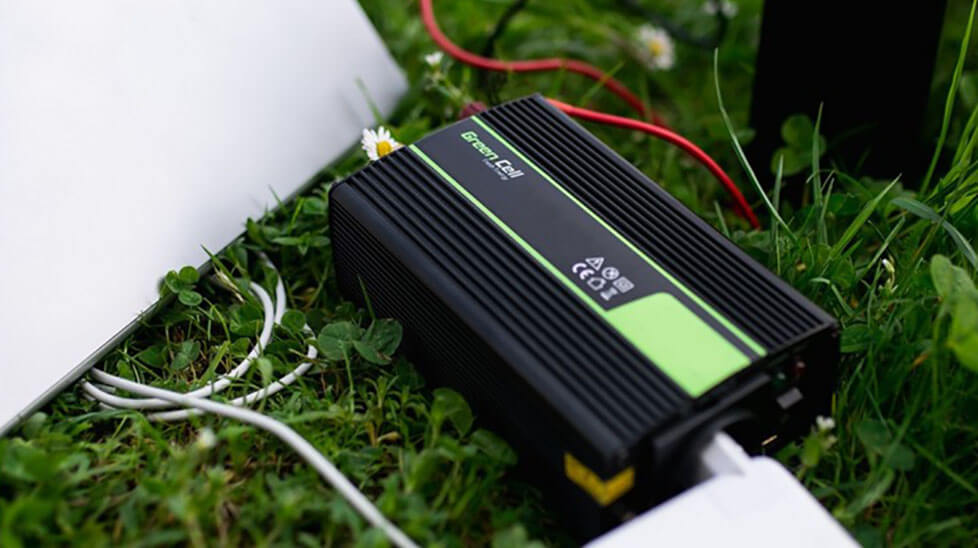
Because car batteries supply DC voltage and most consumer electronics operate on AC current, you need a device known as a voltage converter. With a voltage converter installed, you can take virtually any electronic device from your home or office and use it in your car.
The limitations of a voltage converter to keep in mind are factors such as the capacity of the car battery, the power output of the alternator and the output power of the converter.
The fact is that the electrical system in your car can only supply a finite amount of current and the battery can only supply so much before it runs out of power, so all of these factors can all play a part in determining which devices can be connected to a car. inverter and used on the road.
How do inverters work?
Inverters work by using a unidirectional DC power source to mimic an alternating current (AC) source. Electronic converters are essentially oscillators that quickly switch the polarity of the DC power source, effectively creating a square wave.
Since most consumer electronics require a true sine wave, most inverters include additional components that create a modified or pure sine wave.
Who needs a car inverter?
Anyone who spends a lot of time on the road can benefit from some kind of inverter. These devices are especially useful on long road trips, camping, business travellers, truck drivers and other similar applications.
Some devices, such as cell phones and laptops, can be used with 12V sockets that plug directly into a cigarette lighter or accessory sockets. However, any electronic device that requires an AC input calls for an inverter. Some devices that you can run on a car inverter are:
televisions
DVD and Bluray players
Game Systems
Catalytic heaters
cooking equipment
Electrical tools
What are the Different Types of Car Inverters?
There are a number of different types of inverters, but the two main ones are:
Modified Sine Wave
These inverters are the more affordable of the two. They produce a "modified sine wave" which is fine for most consumer electronics.
Pure sine wave
These are usually more expensive, but they produce a sine wave that is much closer to the AC current from the outlets in your home. Some appliances, such as uninterruptible power, may not work well without a stable, pure sine wave, but most consumer electronics will work fine without one. If you have any concerns, please contact us before investing in an expensive pure sine wave inverter.
How are inverters connected?
In order to work, an inverter must be connected to the car battery in some way. Some of the most common configurations are:
Fuse panel
Direct on battery
Via Lighter
Via the 12V socket
The easiest way to hook up an inverter is to simply plug it into the cigarette lighter or other 12V outlet, but there are some limitations to those types of configurations.
Since there may be other components connected to the cigarette lighter or accessory circuit, there is a limitation on what type of devices can be connected to the inverter. Inverters connected in this manner are typically limited to 5 or 10 amps.
In heavier applications, the inverter must be connected to the fuse panel or directly to the battery. Some fuse panels have empty slots into which an inverter can be plugged. This provides a special circuit for the device. In other cases, the inverter can be connected directly to the battery with a built-in fuse. In either case, it is vital to use some sort of fuse to avoid a potentially dangerous situation.
Additional Considerations
Since most cars and trucks aren't really designed with inverters in mind, it's important to avoid overloading the system. A crucial factor to consider is the capacity of the battery. If an inverter is used while the vehicle is not moving, it tends to drain the battery quickly.
Some trucks have extra space under the hood for an extra battery, which can help reduce the impact of using an inverter when the vehicle is not running, but that's not always an option.
While using an inverter while the vehicle is moving, the alternator needs to fill the battery, it is also vital to avoid overloading the alternator. Because alternators are typically designed to provide enough power to run all the electronics in a vehicle and keep the battery charged, they may not have enough additional capacity to run a powerful inverter.
The best way to avoid a problem in this area is to check the power of your alternator and then buy a suitable inverter. If that's not enough, there may be an OEM option for a higher output alternator. Aftermarket units that deliver even more power are also sometimes available.